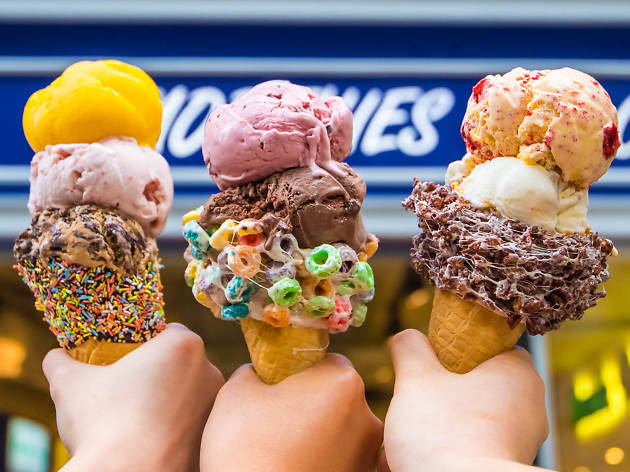
Emack & Bolios, a Boston based ice cream company recently partnered up with premier cannabis brand, MariMed. The pair have plans to collaborate and launch a lineup of Cannabis-infused ( & vegan too) ice cream, in their words – outrageous flavors. I’m a simple person, Nutella or pistachio will be more than fine thank you! I don’t really want fruit loops hanging off my ice cream.
Little is known about these outrageous flavors that will be coming to dispensaries. However it’s said that consumers will see the very same terpenes and cannabinoids which derive from their high quality flower and their award winning products implemented in the recipes. It also won’t be your standard ice cream with THC but rather some of the companies highest quality concentrates will be going into the end product.
“We’ve taken great care to grow MariMed infused products to become top-selling brands, with much of our success the result of a craft-like approach to cultivation that is unlike most other national cannabis companies,” MariMed CEO and President Bob Fireman said in a prepared statement.
“We’re excited to bring our unique formulations and technologies to a collaboration with a brand partner like Emack & Bolio’s, which has such a fantastic history.”
Bob Rook the man who founded Emack & Bolios, started the company in 1975 for his rock star clients – he was a music attorney at the time – so they can enjoy ice cream after late night gigs. Some of those stars go by the name of Aerosmith, Boston, U2 & James Brown.
You’re probably wondering when and where the new ice cream flavors are available, unfortunately the company advised that they are looking for a late 2021 launch.
Where Can I get Cannabis Infused Ice Cream From?
Although this isn’t the first company to bring infused ice cream, a special mention to Cloud Creamery who launched their range of infused ice cream sometime in June and guess what? It’s available – see below:
Cloud Creamery has decided to start with three flavors that include two types of ice cream, Tanzanian vanilla and dark chocolate truffle, and one sorbet, mango yuzu, which is dairy-free. The vanilla is actually sourced from Tanzania.